Ionization of Acids and Bases
Ionization of Acids and Bases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Dissociation of Bases in Water, Relationship between Degree of Dissociation and Dissociation Constant of Weak Acid & Relationship between Degree of Dissociation and Dissociation Constant of Weak Base etc.
Important Questions on Ionization of Acids and Bases
The of acetic acid solution is closest to [Dissociation constant of the acid, ]
Which of the following equation follows for base ionization constant is expressed in terms of concentration in molarity of various species in equilibrium.
Calculate the concentration of ions in the solution of .
Ionisation constant of is and concentration of ions is . Then, the initial concentration of is
Which of the following will occur if a solution of a weak acid is diluted to at constant temperature?
The values of formic acid and acetic acid are respectively and . The ratio of acid strength of acids is
Which of the following is a weak alkali?
The of an aqueous solution of is
is dissolved in water.
Its base dissociation constant is given by:
Select the weak base from the following:
The increasing order of base strength is
A aqueous solution of a monobasic acid had a freezing point change of What is the for the acid? Given that molal depression constant of is
Arrange in decreasing order of acidity?
(P) 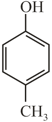 (Q)
(Q) 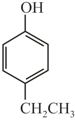 (R)
(R) 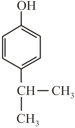 (S)
(S) 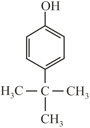
The correct order of increasing in the following aqueous solution is
What is the decreasing order of strength of bases?
What will be the of a solution obtained by diluting of weak monoacidic base to at constant temperature if the dissocitaion constant of the base is ?
If solution of a weak acid is diluted to at constant temperature, then corresponding consequence is:
Calculate equilibrium constant for weak acid reaction with strong base if weak acid shows .
Initial pressure of is 800 mm and total pressure at equilibrium is 900 mm of Hg. Calculate the percentage of dissociated in the following reaction:
